There are different types of buildings based on their purposes. Buildings are constructed for, hospitals, schools, offices, banks, etc. These types of buildings are very critical and important to make stronger against earthquakes.
There may loss of property and life for the sudden collapse of the building. Earthquake applies lateral force to the building which makes the building weak in lateral resistance. Hence, it is important to make the Earthquake proof a building. Here I have described some requirements of earthquake resistance building.
The important characteristics that any earthquake resistant structure should possess are,
1) Adequate stiffness and strength
2) Ductility and toughness
3) Regularity
4) Continuous load path
5) Redundancy
6) Stable foundations
1) Adequate stiffness and strength
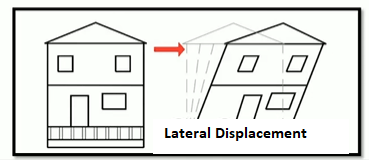
Strong earthquakes will induce both vertical and lateral forces in a structure.
There is more probability of structure being damaged if there is acting horizontal force than compressive to tensile force.
So, to avoid the structure from lateral displacement and instability, the structure must possess a sufficient amount of lateral stiffness as well as lateral strength.
- Hence a structure should possess adequate strength to resist both gravity and lateral loads.
- The structure should also posse.s adequate lateral stiffness to limit the deflections.
2) Ductility and toughness
Ductility and toughness are structural properties that relate to the ability of a structural element to sustain damage when overloaded while continuing to carry the load without failure. This arc has extremely important properties for structures designed to sustain damage without collapse.
- Most structural elements are designed to provide sufficient strength to support anticipated loads without failure and enough stiffness so that they will not deflect excessively under these loads,
- Masonry and concrete will crush when overloaded in compression and will crack and pull apart when placed in tension or shear.
- Wood will crush when overloaded in compression, will split when overloaded in shear, and will break when overloaded in tension. Steel will buckle if overloaded in compression and will twist when overloaded in bending if not properly braced, but will yield when overloaded in tension.
3) Regularity
A structure is regular if the distribution of its mass, strength, and stiffness is such that it will sway in a uniform manner whenever lateral force to an earthquake shakes the ground.
Hence for a regular structure, the lateral movement in each storey(elevation), and on each side of the structure (plan) will be about the same.
- Regular structures tend to dissipate the earthquake’s energy uniformly throughout the structure resulting in relatively light but well-distributed damage.
- An irregular structure has many small components to connect the whole structure. This causes several joints in the structure. The joints in the structure may possed several negative bending moments in the structure, which may cause an increase in damage due to lateral forces in the building or structure.
4) Continuous load path
The continuous load path is a very important point to be considered for earthquake resistance building. All the components and members like beams, columns or slabs should be tied together to act as a single structure.
This provides a continuous path to the structure that will transfer the inertial forces to the ground due to earthquakes in the building.
If all the components of a building or structure are not tied together in this manner, the individual pieces will move independently and can pull apart, allowing partial or total collapse to occur.
5) Redundancy
If all of a structure’s strength and resistance is concentrated in only one or a few elements, the structure will not have any residual strength if these elements are seriously damaged and could collapse.
A redundant structure consists of many elements to provide strength to the structure to withstand. In this case, if one or two members got damaged, then another member will bear the strength of the structure and prevent it from collapsing.
6) Stable foundations
In addition to the excessive settlement, the foundation system must be able to resist earthquake-induced overturning forces and be capable of transferring large lateral forces between the structure and the ground.
On sites that can be subjected to liquefaction or lateral spreading, it is important to provide vertical bearing support for the foundation beneath the liquefiable layers of soil.

Foundation should be flexible as far as possible. The flexible foundation of the building makes the foundation act as a spring. So, while an earthquake, the building does not have to bear sudden jerk to the breakdown of the concrete member.
A flexible foundation observes the vibration and seismic waves and resists passing through the building.
Happy Learning – Civil Concept
Read Also
What is cause of Earthquake | Effects of Earthquake
21 Rules to Construct earthquake resistant buildings – Guidelines
